Please! This is work in progress…
See change log below for updates and additions…
ALSO this is being split into sub-pages now as it is getting too big!
The Brexit in/out campaign is getting incredible dirty and full of propaganda and lies so here I have been trying to find facts only.
Please tell me if something is incorrect.
Index to subpages:
- VAT
- Environment
- Free movement of persons (former section on immigration)
- Employment
- Business
- Economy
- Economy of Brexit
- Banking and Currency
- Article 50
- Quangos
- Brexit Leaflet
- The Results
Diplomatic Mission9
The member states of the European Union speak with the same voice on many issues. The EU is the world’s largest trade bloc and donor of humanitarian and development assistance, and thus has an extensive network of delegations around the world mainly operating in the framework of External Relations, for which the European Commission is the main decision body.
The EU has 140 ‘delegations’ – EU embassies – around the world, each with ‘Heads of Delegations’ – EU Ambassadors – making up the European External Action Service – the EU’s foreign service.
EU Budget
The European Union has a budget to pay for policies carried out at European level (such as agriculture, assistance to poorer regions, trans-European networks, research, some overseas development aid) and for its administration, including a parliament, executive branch, and judiciary that are distinct from those of the member states.
EU budget is combined by contributions based on the GDP and tax on VAT (yes tax on tax!).
EU contributions per capita in 2014 (23):
- United Kingdom €229 (thanks to the rebate originally negotiated by Margaret Thatcher in 1984)
- Denmark €487 (similar to Norway)
- Spain €232
- Germany €353
- France €332
EFTA contributions to EU per capita in 2014 (23):
- Switzerland €68 (EU export 45% 22)
- Norway €107 (EU export 63% 21)
- Iceland €50 (EU export 78% 20)
Interesting note in (23) on EFTA:
After 50 years of existence, the European Free Trade Association is still a political and economic alternative for European countries, which want to remain outside the European Union. The reasons for being a member state of EFTA are today exactly the same as they were 50 years ago: EFTA states can maintain their independent monetary policy, foreign affairs, defence and agriculture and fisheries policies. On average, EFTA states enjoy a higher GDP per capita and a lower unemployment rate than the EU-28.
Questions to be asked:
- As Switzerland is landlocked with the EU the UK should have an even better deal than Switzerland if we left the EU?
- If a country do better then they have to pay more EU contributions – does that encourage a prudent national budget approach?
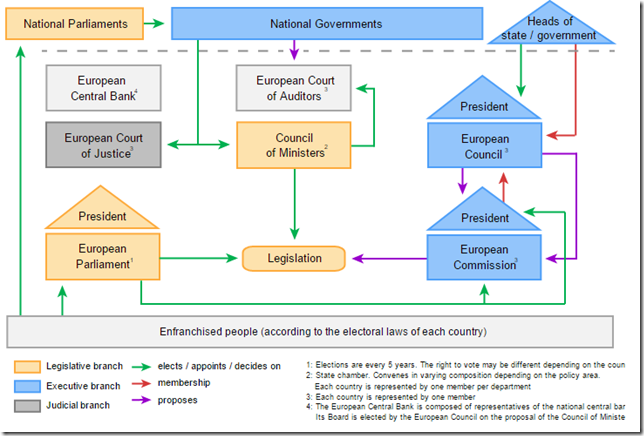
Governance
This is quite messy but here is an overview (click to enlarge):
The details:
- European Commission: Unelected executive branch. Responsible for initiating all legislation and the day-to-day running of the EU. 28 Commissioners for different areas of policy – one Commissioner from each member state, though Commissioners are bound to represent the interests of the EU as a whole rather than their home state. Any legislation presented by the Commission must be voted upon by the European Parliament. The commission has powers to pass certain sensitive matters without the approval from the parliament like laws on taxes
- European Parliament: Elected primary chamber. The European Parliament forms one half of the EU’s legislature (the other half is the Council of the European Union). The 751 Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are directly elected by EU citizens every five years on the basis of proportional representation. Parliament and the Council of the European Union pass legislation jointly
- Council of the European Union: Second chamber. Forms the other half of the EU’s legislature. It consists of a government minister from each member state and meets in different compositions depending on the policy area being addressed.
- European Council: The European Council gives direction to the EU, and convenes at least four times a year. It comprises the President of the European Council, the President of the European Commission and one representative per member state; either its head of state or head of government. The European Council has no legislative power
- Court of Justice of the European Union: Ensure uniformity of interpretation of European law and has the power to decide legal disputes between EU member states, EU institutions, businesses and individuals
- European Central Bank ECB: forms together with the national central banks the European System of Central Banks and thereby determining the monetary policy of the EU and EURO
- European Court of Auditors: EU budget is scrutinised by the auditors however they do not audit the EU finances
All the above institutions are based mainly in Brussels, Luxemburg (court and auditors) and the ECB in Frankfurt
Trade(13)
There is a lot of statistics in this area and it is generally hard to interpret.
The graph below includes both goods and services.
If you look at the proof in the pudding then the EU trade had fallen by around 10% since 1999 (see dotted line) and continue to fall.

Negative EU balance means the EU is dependent on exporting to the UK as well as the UK is increasingly dependent on exporting outside the EU = non-EU.
Not that clear from the graph above but another article has analysed the net trade balance details from above and come to same conclusion (14) but in a clearer way:

It get even more complicated as some of the EU trade is actually non-EU trade (3). For example goods exported from the UK are often sent via the Netherlands to Rotterdam and from there to the final destination outside the EU. So this trade looks like EU trade where in fact it is non-EU trade. To quantify this is complicated but the amounts are significant if looking at the UK to Netherlands trade figures.
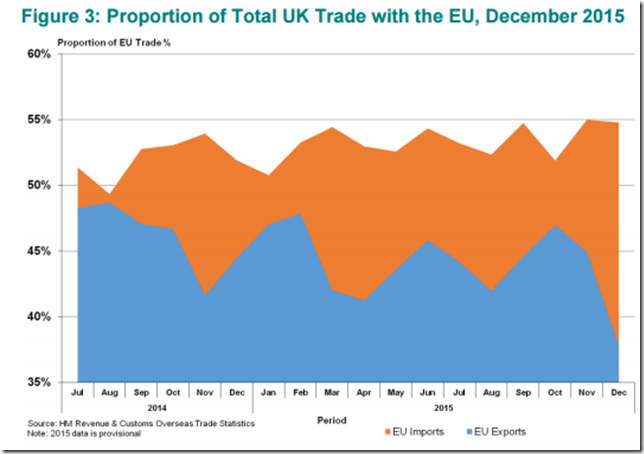
December 2015 Trade numbers35:
- Non-EU exports increased 22%
- Non-EU imports down 11%
- Total exports to non-EU is now 62%
- Total imports from non-EU is 45%
- EU exports down 7.7%
- EU imports down 6.3%
- Total exports to the EU is now 38%
- Total imports from the EU is 55%
So the UK activity with the EU is falling dramatically!
Questions to be asked:
- How much EU trade is “artificial” due to subsidies resulting in situations like how it can be cheaper to fly tomatoes from Spain to the UK rather we grow then ourselves?
- How can EU trade be falling since 1999, while the number of EU countries has expanded from 15 to 28 in same timeframe (bigger EU = less trade to UK?)?
- If the trend continues would we be playing on the right horse by being in the EU?
Tax (12)
This is a complex subject due to the various ways people and businesses are taxed in the EU and EFTA.
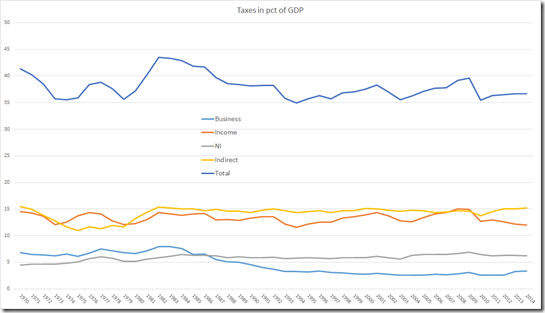
UK tax since 1970:
No impact of the UK entering the EU. Also business tax has dropped since late eighties over both successive left and right governments.
Total EU and non-EU taxes in PCT of GDP:
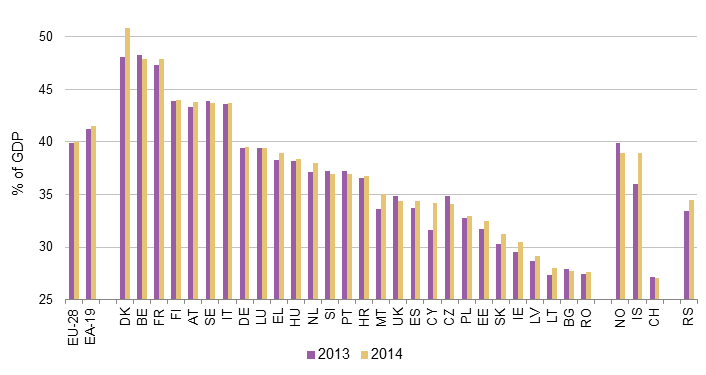
Switzerland (CH) has a very low tax compared to the EU almost as low as Romania (RO) although preserving a high-level social system.
Double Irish/Dutch Sandwich39
Typically, the company arranges for the rights to exploit intellectual property outside the United States to be owned by an offshore company.
Example:
- An advertiser pays for an ad in Germany
- The ad agency sends money to its subsidiary in Ireland, which holds the intellectual property (IP)
- Tax payable in Ireland is 12.5 percent, but the Irish company pays a royalty to a Dutch subsidiary, for which it gets an Irish tax deduction
- The Dutch company pays the money to yet another subsidiary in Ireland, with no withholding tax on inter-EU transactions
- The last subsidiary, although it is in Ireland, pays no tax because it is controlled outside Ireland, in Bermuda or another tax haven
In 2014, the Irish government announced that companies would no longer be able to incorporate in Ireland without also being tax resident there, a measure intended to counter arrangements similar to the double Irish. Irish Finance Minister Michael Noonan addressed the “Double Irish” during the presentation of his 2015 budget. Under the new rules, companies not already operating in the country may not pursue the “Double Irish” scheme as of January 2015; those already engaging in the tax avoidance scheme have a five-year window until 2020 to find another arrangement
Under Finance Act 2015, a new system has been introduced whereby innovative companies who choose to incorporate in Ireland can now benefit from the introduction of the Knowledge Development Box (the “KDB”) in Ireland, the scheme is seen a replacement for the “double-Irish” tax system which was recently closed. An effective tax rate of 6.25% can be obtained on qualifying profits generated in periods commencing on or after 1 January 2016.
Questions to be asked:
- In many EU reports Switzerland is left out for reasons, which can be interpreted as obvious as they have a very low tax indeed?
Most of the time EU taxes are compared to Norway and Iceland, which are both part of the highly taxed Nordics/Scandinavia - How can a country like Switzerland with with high-level of social security have as low taxes as Romania?
- How can the EU allow tax avoidance between two EU countries like in the Irish/Dutch sandwich?
Legal System
EFTA Secretariat, the EU generated 52,183 legal instruments between 2000 and 2013.
The all have to be adopted by EU members.
EFTA uptake (5):
- Norway: adopted 4,724 – 9 per cent
- Iceland: adopted 6,326 out of 62,809 EU legal acts between 1994 and 2014 – 10%
- Switzerland: zero per cent
Difference between European Court of Justice and European Court of Human Rights(10)
- European Court of Justice ECJ rules on European Union (EU) law
- European Court of Human Rights ECHR rules on European Convention on Human Rights which covers the 47 member states of the Council of Europe CE
The EU’s Treaty of Lisbon, in force since 1 December 2009, requires the EU to accede to the convention in Article 6 of the consolidated Treaty on European Union.
In other words UK can only avoid ECHR if outside both EU and CE.
European Court of Human Rights can rule against deportation if a person faces death sentence, torture or unfair trial (11).
Questions to be asked:
- Seems like Switzerland can get away with having a extensive trade union without committing to any EU laws. Maybe Switzerland has a more negotiation power compared to Norway and Iceland. Maybe this would work in the favour of United Kingdom?
Military System
- This is not applicable to EU as this is fully covered by NATO
- The EU has some peacekeeping and European Border and Coast Guards (former Frontex) to detect and stop illegal immigration, human trafficking and terrorist infiltration
- United Kingdom permanent membership of the UN Security Council(17) is based on the outcome of WWII and is not dependent on economics nor membership of the EU
Questions to be asked:
- Why paying to a EU military force when we are already paying to a NATO force?
- Still need to understand why the EU need a border force when this according to the Schengen agreement should be done my the individual member state?
- Many says the EU have secured our safety since WWII but is it not really NATO including the US that have done that?
History1
- 1957 – EEC (Rome treaty created) by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and West Germany (total 6 countries)
- 1973 – Denmark, Ireland and United Kingdom joins (total 9 countries)
- 1981 – Greece joins(total 10 countries)
- 1986 – Portugal and Spain joins (total 12 countries)
- 1993 – Maastricht treaty created leading to the EURO
- 1995 – Austria, Finland and Sweden joins (total 15 countries)
- 2002 – EURO introduced in 12 countries simultaneously
- 2004 – Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta,Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia joins (total 25 countries)
- 2007 – Romania and Bulgaria joins (total 27 countries)
- 2009 – Lisbon treaty created introducing majority voting in the EU parliament
- 2013 – Croatia joins (total 28 countries)
Turkey(18) is to join next but is being held back due to mainly Germany. Germany already has a large Turkish population(19), which may explain the reluctance. However in the current refugee crisis Turkey has been using the flow of refugees as a negotiation weapon.
Iceland(20) withdrew its application to the EU membership 12 March 2015. EU would have limited the fishing in Iceland where their current membership of EEA does not limit this.
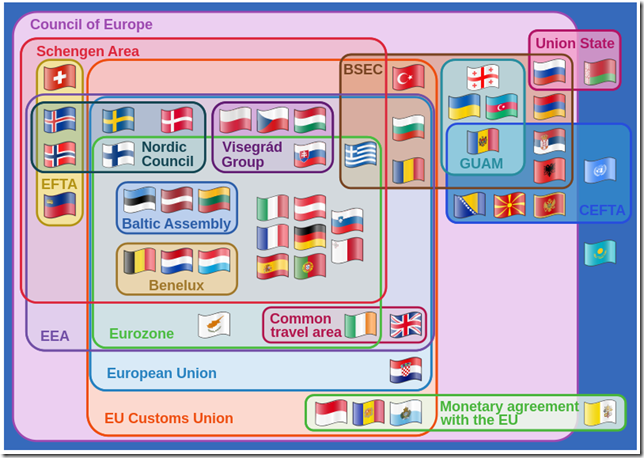
Countries not in the EU (but often mistakenly included or confused in relation to EU):
- EFTA2 countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland
- EEA3 countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway providing free movement of persons, goods, services and capital within the EU
- Turkey customs union4: Goods may travel between the two entities without any customs restrictions. The Customs Union does not cover essential economic areas such as agriculture (to which bilateral trade concessions apply), services or public procurement
Questions to be asked:
- How can we keep control the borders to Turkey if they become an EU member – just try to have a look at a map of Turkey – it is missive and impossible to control hence the current refugee crisis?
- Leaving EU and being in the EEA instead would strengthen UK fishing just like Iceland?
Overview of European Organisations (click to zoom):
Good Articles (subscripted)
- Legal: http://blogs.spectator.co.uk/2016/02/what-britain-would-look-like-after-brexit/
- Legal: http://eureferendum.com/blogview.aspx?blogno=85798
- Trade: http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/63fe7f64-da16-11e5-a72f-1e7744c66818.html
- Scotland: http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-scotland-scotland-business-35301158
- Immigration: http://www.theoccidentalobserver.net/2013/07/the-labour-partys-immigration-treason-selling-out-the-white-working-class/
- Immigration: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/newstopics/eureferendum/12184083/David-Cameron-must-release-figures-showing-full-scale-of-EU-migration-Cabinet-minister-says.html
- Banking: http://bankingunion.eu/
References (superscripted)
- EU: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Union
- EFTA: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Free_Trade_Association
- EEA: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Economic_Area
- Turkey: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Union%E2%80%93Turkey_Customs_Union
- http://blogs.spectator.co.uk/2016/02/what-britain-would-look-like-after-brexit/
- Budget: http://www.money-go-round.eu/
- Immigration: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/migration1/migration-statistics-quarterly-report/february-2016/sty-net-migration.html
- Immigration: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/about-ons/business-transparency/freedom-of-information/what-can-i-request/previous-foi-requests/population/illegal-immigrants-in-the-uk/index.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_diplomatic_missions_of_the_European_Union
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relationship_between_the_European_Court_of_Justice_and_European_Court_of_Human_Rights
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Convention_on_Human_Rights
- Personal tax: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Tax_revenue_statistics
- Trade: http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20160105160709/http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/international-transactions/outward-foreign-affiliates-statistics/how-important-is-the-european-union-to-uk-trade-and-investment-/sty-eu.html
- Trade: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/economics/11661581/Trade-deficit-shrinkage-set-to-boost-UK-growth.html
- Moved to Economy
- Moved to Economy
- Military: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_Nations_Security_Council
- Turkey: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accession_of_Turkey_to_the_European_Union
- Turkey: http://www.migrationpolicy.org/article/turkey-transformation-emigration-immigration
- Iceland: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accession_of_Iceland_to_the_European_Union
- Norway: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Norway
- Switzerland: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Switzerland
- Budget: http://iasir.net/AIJRHASSpapers/AIJRHASS14-306.pdf
- Migration: http://www.migrationwatchuk.org/statistics-net-migration-statistics
- Migration: http://www.migrationpolicy.org/article/united-kingdom-reluctant-country-immigration
- Moved to Banking
- Moved to Banking
- Moved to Banking
- Moved to Employment
- Moved to Business
- Moved to VAT
- Moved to VAT
- Moved to VAT
- Moved to VAT
- Trade – 2015: https://www.uktradeinfo.com/Statistics/OverseasTradeStatistics/Pages/EU_and_Non-EU_Data.aspx
- Moved to Business
- Moved to VAT
- Moved to VAT
- Tax- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double_Irish_arrangement
- Moved to Economy
Change log:
- 27/2: Created document
- 28/2: Added Economy in GDP and added some questions around migration
- 29/2: Added fact about UK in UN Security Council and Turkey as next in the EU and Iceland reason not to be in the EU
- 1/3: Updated EU budget contributions to 2014 numbers. Added more info to Migration
- 8/3: Added Employment and Employers
- 9/3: Added VAT
- 10/3: Added 2015 trade figures
- 10/3: Created separate VAT page
- 10/3: Created separate environment page
- 15/3: Separated employment into separate page
- 20/3: Separated Employers into separate page