This is part of the EU Fact File
Verdict: OUT – Even though the UK is not in the EURO zone we are still impacted by the Banking Union – limiting what we can do with our banks and financial industry. It is proven by banking outside the EU is growing rapidly whilst both the UK and Germany seems stagnant. Outside the EU we can still help the EU if needed without being overly exposed thanks to the IMF. The involvement of the IMF in bailing out both Greece, Cyprus, Portugal and Ireland proves the inability of the ECB and EU to deal with the EURO crisis.
The UK is not in the EURO zone (blue) as per below (click to get more info 1):
However being in the EU still affects the UK:
- Many directives impact the UK banking sector due to EU directives in spite of the UK not being in the EURO zone (2)
- The UK is a member of the EU banking union
- For example in 2015 we had to lower our savers deposit guarantee from £85.000 to £75.000 due to the European Deposit Guarantee Schemes Directive (DGSD) 2
- Since 2011 banking assets in the UK banking sector have shrunk by 12% (5% in wholesale) while growing in rival centres: by 12% in the US, 34% in Hong Kong and 24% in Singapore. Over the same period, employment in the UK banking sector has fallen by 8% (35,000) 3:
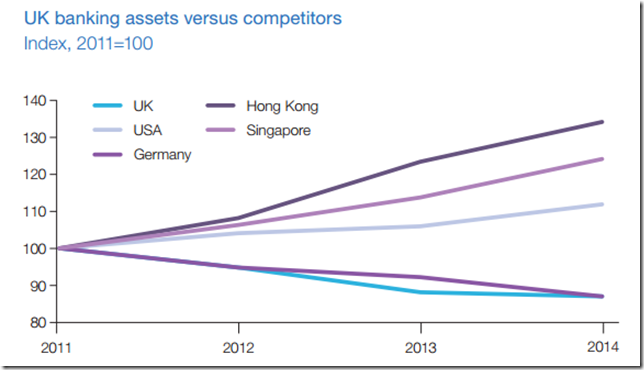
Graph explains why banks not are contemplating going to the EU like Germany (Frankfurt is often mentioned in pro-EU arguments)
EU Banking Union
In response to the financial crisis that emerged in 2008, the European Commission pursued a number of initiatives to create a safer and sounder financial sector for the single market. These initiatives, which include stronger prudential requirements for banks, improved depositor protection and rules for managing failing banks, form a single rulebook for all financial actors in the 28 Member States of the European Union. The single rule book is the foundation on which the Banking Union sits10.
The UK is a member of the Banking Union.
European Stability Mechanism – ESM and European Financial Stability Facility – EFSF
The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) was created as a temporary crisis resolution mechanism by the euro area Member States in June 2010. The EFSF has provided financial assistance to Ireland, Portugal and Greece. The assistance was financed by the EFSF through the issuance of bonds and other debt instruments on capital markets9.
This was replaced by the ESM in 20128.
The European Stability Mechanism is the crisis resolution mechanism for countries of the euro area. The ESM issues debt instruments in order to finance loans and other forms of financial assistance to euro area Member States.
The UK is not a member of the EFSF or ESM as it only applied to EURO countries (in blue below)8.
World Bank
The World Bank is not involved in the EU but are often mentioned in connection with the IMF as both are UN institutions7.
The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank were both created at an international conference convened in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States in July 1944.
The World Bank’s mandate. The World Bank promotes long-term economic development and poverty reduction by providing technical and financial support to help countries reform particular sectors or implement specific projects—such as, building schools and health centres, providing water and electricity, fighting disease, and protecting the environment
International Monetary Fund – IMF
We cannot look at the EU without also considering the role of IMF as they keep commenting on EU and UK policies.
The purpose of the IMF is7:
The IMF’s mandate: The IMF promotes international monetary cooperation and provides policy advice and technical assistance to help countries build and maintain strong economies. The IMF also makes loans and helps countries design policy programs to solve balance of payments problems when sufficient financing on affordable terms cannot be obtained to meet net international payments.
However in reality the IMF is not following it’s original purpose.
Looking at Greece has €21.2 billion in outstanding obligations to the IMF5. Additionally also Portugal and Ireland has significant debt6.
Due to the IMF lending to EU countries having the EURO and member of the IMF is not just the Eurozone countries – the IMF widens the EURO exposure beyond the Eurozone.
Essentially the UK is being dragged into the EURO via the IMF. The UK direct exposure to the Eurozone is hard to gauge however2.
Even if the UK left the EU – the UK would still be exposed to the EU however being in the EU and even worse in the EURO would increase the exposure significantly via the EFSF/ESM (see above).
European Union financial transaction tax – Tobin Tax
The European Union financial transaction tax (EU FTT) is a proposal made by the European Commission to introduce a financial transaction tax (FTT) within some of the member states of the European Union initially by 1 January 2014, later postponed to 1 January 2016 and then to Mid 201611.
Strangely delayed until after the UK Brexit vote.
According to early plans, the tax would impact financial transactions between financial institutions charging 0.1% against the exchange of shares and bonds and 0.01% across derivative contracts, if just one of the financial institutions resides in a member state of the EU FTT.
Hence a tax like this would impact all global transactions originating in the UK.
Currently the UK expect to have to veto this tax.
The tax would be levied on all transactions on financial instruments between financial institutions when at least one party to the transaction is located in the EU. It would cover 85% of the transactions between financial institutions (banks, investment firms, insurance companies, pension funds, hedge funds and others).
House mortgages, bank loans to small and medium enterprises, contributions to insurance contracts, as well as spot currency exchange transactions and the raising of capital by enterprises or public bodies through the issuance of bonds and shares on the primary market would not be taxed, with the exception of trading bonds on secondary markets.
This would essentially be the death of London based insurance companies and international banking. For a bank like HSBC a move to Hong Kong would be a no brainer. Similar for insurance company like Lloyds that insure internationally like ships.
Questions to be asked:
- Why can we not have our own deposit guarantee rules – why does it need to be “harmonised” – why not just a minimum?
Countries compete on taxes and VAT why not bank guarantees?
Maybe deposits are larger in the UK (than for instance Romania!!!) so why not our own guarantee level? - If EU is a great place for banks why do HSBC continuously consider moving to Hong Kong (and not somewhere in the EU?
- To compete with USA, Hong Kong and Singapore it seems like it is better to be outside the EU as both UK and Germany has been suffering within?
- Why does the IMF need to bailout a “strong” trade block like the EU and Eurozone as the ECB should be big enough for this purpose?
Good Articles (subscripted)
- http://www.zerohedge.com/news/2015-07-10/john-taylor-imf-loans-greece-bailed-out-banks-and-worsened-situation
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-33165580
References (superscripted)
- https://en.wikipedia./orgwiki/Eurozone
- http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/pra/pages/authorisations/fscs/bankingandsavings.aspx
- https://www.bba.org.uk/publication/bba-reports/winning-the-global-race-2/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Monetary_Fund
- https://www.imf.org/external/country/grc/greecefaq.htm
- http://www.business-standard.com/article/economy-policy/top-10-debtor-countries-owe-86-of-total-imf-loans-115070600274_1.html
- http://www.imf.org/external/np/exr/facts/imfwb.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Stability_Mechanism
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Financial_Stability_Facility
- http://ec.europa.eu/finance/general-policy/banking-union/index_en.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Union_financial_transaction_tax
Change Log
- 15/4-2016: Page created from EU Fact File

